Set up managed identity for Power Platform Plugins
In the following blog, I’m going to guide you on the set up of managed identity for Power Platform. Once we have finished you should have everything you need to be able to create a plugin that can communicate with an azure resource.
Code and blog about plugin package setup
Since the original release of this blog I’ve written a follow up that provides source code and details on plugin packages, Please find it at my blog Power Platform Plugin Package – Managed identity.
Why do we want to use managed identity?
Managed identity allows your plugin to access azure resources, without the need of storing credentials. This is by far the most secure way to extend the reach of your Power Platform plugin into the Azure space.
Documentation
I followed the following Microsoft documentation but hopefully this blog will help bridge some of the gaps I found were missing, I’ve also changed the order to make sure you have what you need when you get to the next step:
Step 1: Create a certificate
You will need a certificate to sign your assembly, as well as the thumbprint for the certificate in the federation settings of your managed identity. I used the following PowerShell:
$ku_codeSigning = "1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.3";
$codeSignCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate `
-Type "CodeSigningCert" `
-KeyExportPolicy "Exportable" `
-Subject "ManagedIdentityPlugin" `
-KeyUsageProperty @("Sign") `
-KeyUsage @("DigitalSignature") `
-TextExtension @("2.5.29.37={text}$($ku_codeSigning)", "2.5.29.19={text}false") `
-CertStoreLocation cert:\CurrentUser\My `
-KeyLength 2048 `
-NotAfter ([DateTime]::Now.AddDays(90)) `
-Provider "Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider";
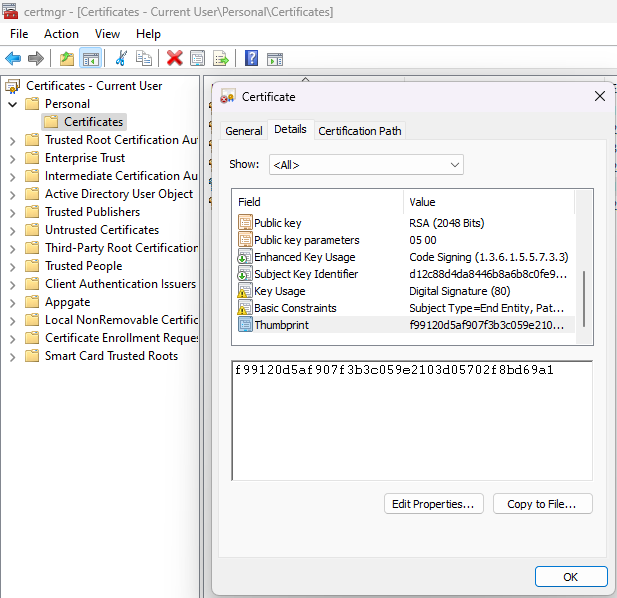
After running this you should have a certificate in current user called ManagedIdentityPlugin.
To see it press Windows & search user certificates, open the “Manage user certificates” option. It should look like this:
Open the certificate and copy the thumbprint.
Step 2: Create a managed identity
-
Go to the Azure portal.
-
Search for managed identity
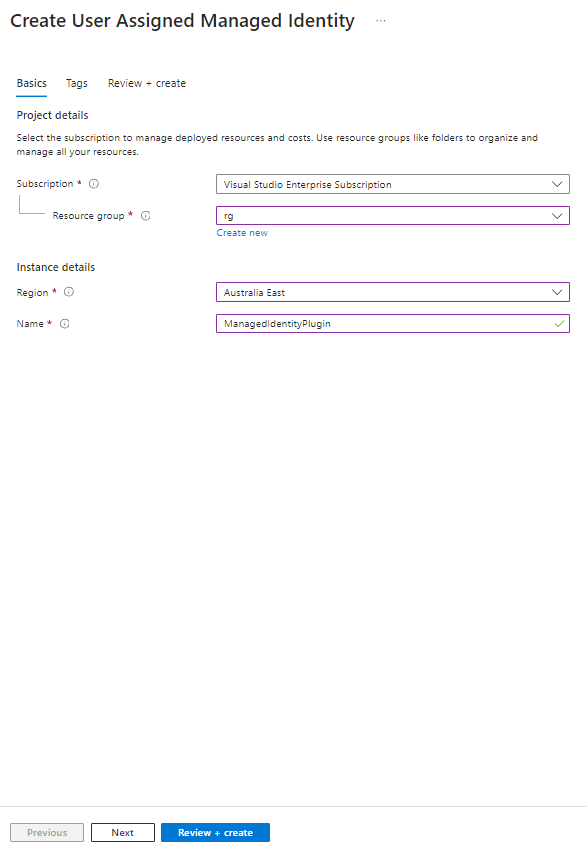
- Create a managed identity (copy the Client ID as we will need this later when we create the record in dataverse)
- Navigate to federated services within the created managed identity and Add Credential
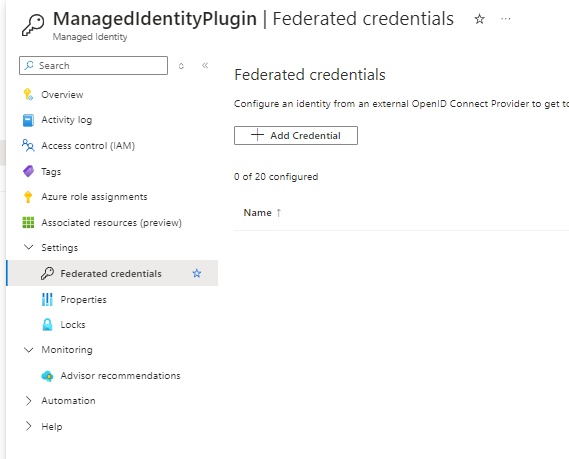
-
Select issuer as Other issuer.
-
Enter the following using your environment ID from PPAC & the thumbprint created before:
Issuer: The URL of the token issuer.
Format similar to this:
https://[environment ID prefix].[environment ID suffix].enviornment.api.powerplatform.com/sts
Environment ID prefix - The environment ID, except for the last two characters.Environment ID suffix - The last two characters of the environment ID.
https://92e1c10d0b34e28ba4a87e3630f46a.06.environment.api.powerplatform.com/sts
Subject identifier: If a self-signed certificate is used for signing the assembly, use only recommended for non-production use cases.
component:pluginassembly,thumbprint:<<Thumbprint>>,environment:<<EnvironmentId>>
Step 3: Assign a role to the managed identity
In my example I’m giving Blob storage data contributor
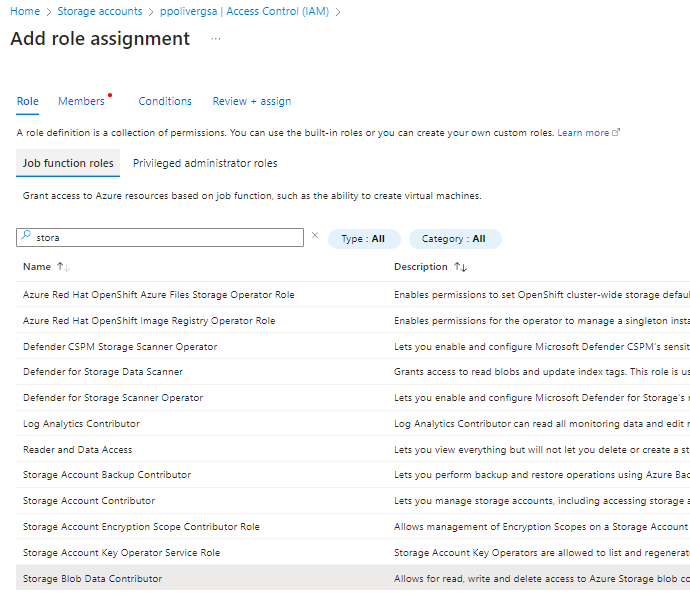
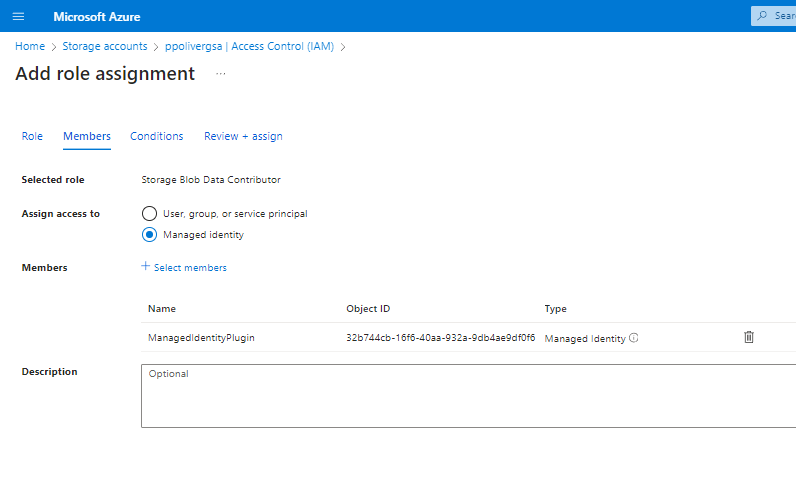
Step 4: Create a plugin
I used pac plugin init
Which can be found here
Within the execute add the following to get a token to your storage account:
var identityService = (IManagedIdentityService)localPluginContext.ServiceProvider.GetService(typeof(IManagedIdentityService));
var scopes = new List<string> { "https://storage.azure.com/.default" };
var token = identityService.AcquireToken(scopes);
Now we can try use that token to query the blob API:
var blobUrl = "https://<your storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/plugin?restype=container&comp=list";
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{ client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", token);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("x-ms-version", "2020-04-08");
HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, new Uri(blobUrl));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.SendAsync(request).Result;
string json = response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result;
localPluginContext.TracingService.Trace(json);
}
Step 5: Build and sign the plugin
For details about signing plugin packages check the next blog.
Build the plugin as you usually would, then you need to sign the plugin using the certificate that we created before. You can either use the following command in the visual studio command prompt in the directory where your dll is located:
signtool sign /n ManagedIdentityPlugin /fd SHA256 ManagedIdentityPlugin.dll
or you can create a post build event in visual studio to do it automatically:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x64\signtool.exe" sign /n ManagedIdentityPlugin /fd SHA256 $(SolutionDir)bin\debug\net462\ManagedIdentityPlugin.dll
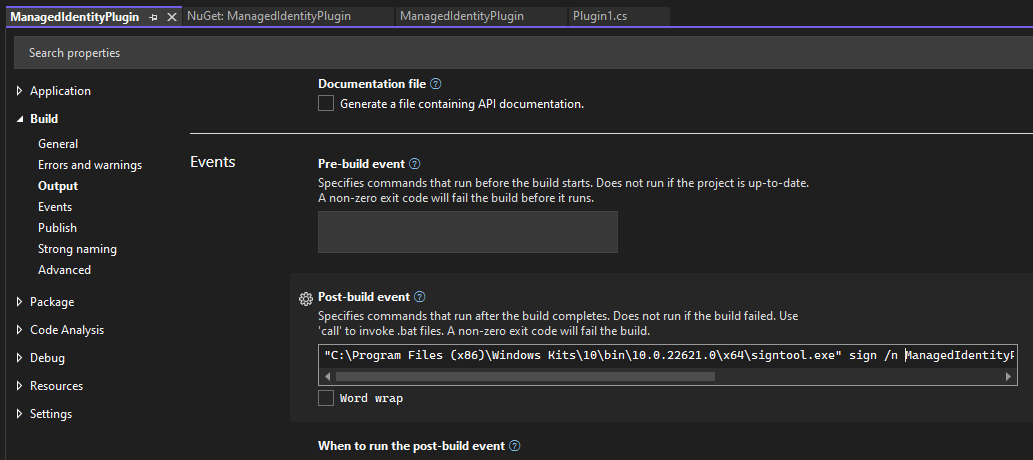
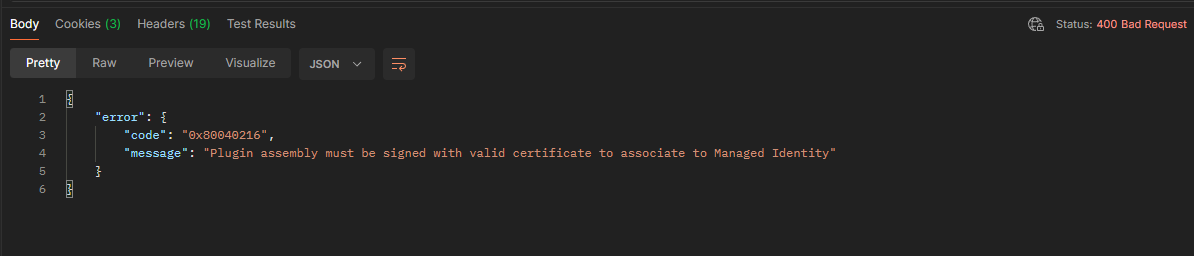
Once you have done this the plugin should look something like this if you check properties on the dll file.
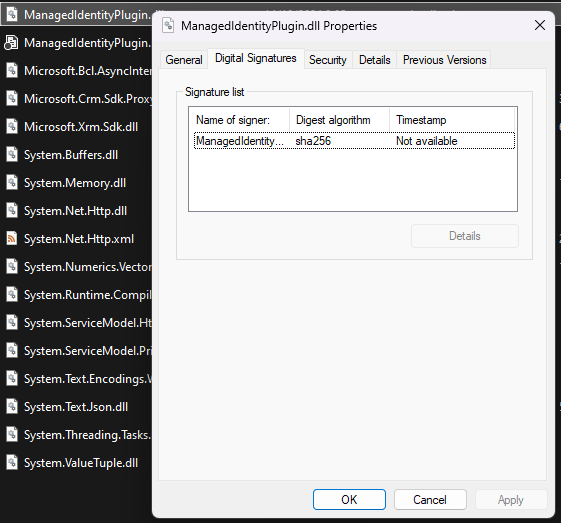
Step 6: Register the assembly
I just used the plugin registration tool, register the plugin and the step you would like it to trigger on. Once it’s registered you need to get the assembly ID, you can find that in the details of the plugin in plugin registration.
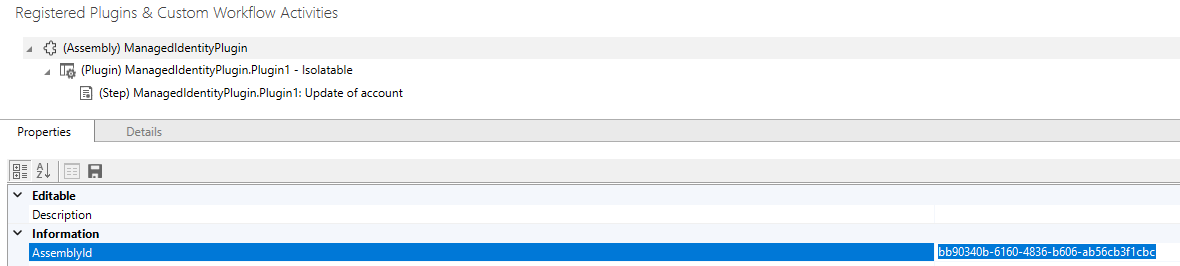
Step 7: Create the managed identity record in dataverse
To do this the documentation is actually quite good.
To provision managed identity record in Dataverse, complete the following steps.
Make an HTTP call using Insomia or any other tool of your choice. You can use a URL with payload in the following format.
POST
https://<orgURL>/api/data/v9.0/managedidentities
Be sure to replace orgURL with the URL of the organization.
Ensure that Credentialsource is set to 2 in the payload and SubjectScope is set to 1 for environment-specific scenarios.
applicationid: Client ID that we copied from the managed identity we created in azure
Managedidentityid: I just used the same Guid as the application ID.
{
"applicationid":"<appId>",
"managedidentityid":"<anyGuid>",
"credentialsource":2,
"subjectscope":1,
"tenantid":"<tenantId>"
}
Here’s the one I did:
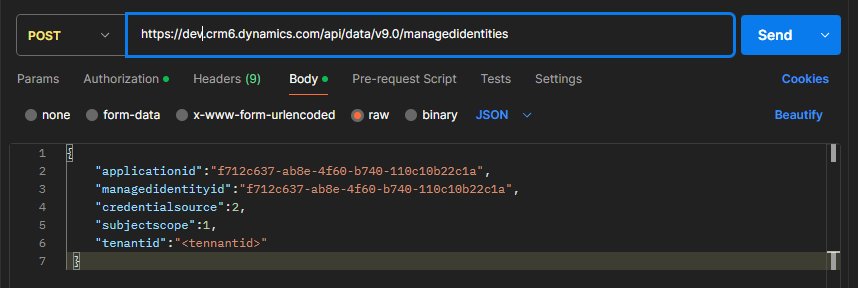
Step 8: Associate your plugin to the managed identity
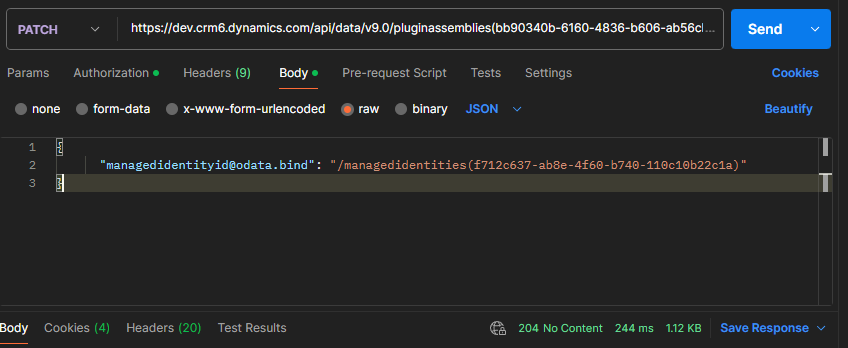
Make an HTTP call to bind the plug-in assembly ID with the managed identity record that’s created in step 7.
Request
PATCH
https://<orgURL>/api/data/v9.0/pluginassemblies(<PluginAssemblyId>)
Body
{
"managedidentityid@odata.bind": "/managedidentities(f712c637-ab8e-4f60-b740-110c10b22c1a)"
}
Be sure to replace orgURL and PluginAssemblyId (the one we found in step 6).
Here’s my example
All that’s left to do is test your plugin!
In my example I’ve just listed the blobs within a container in my storage account. To see this I’ll have a look in the plugin trace logs:
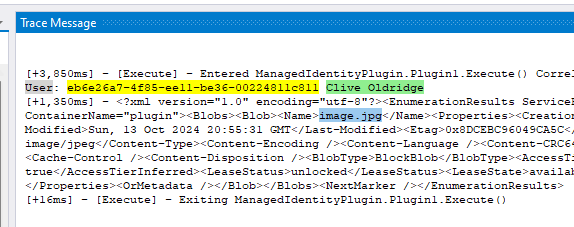
Here we can see that my plugin was successfully able to connect to the storage account without any password/client secret and retrieve a list of files within the container.
Common Issues
I had No matching federated identity record found for presented assertion issuer this was because I forgot to remove the - from the GUID when I created the federation’s settings in step 2.

Another one that can be challenging is “Plugin assembly must be signed with valid certificate to associate to Managed Identity”. Checking the properties of the dll helps you validate this.